Modern medicine is constantly evolving, seeking new ways of providing efficient patient treatment. Global healthcare market is estimated around USD 423.97 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1,445.71 billion by 2034. The healthcare market is one of the most capital and technology intensive with millions of dollars spent only on R&D. One of the key challenges of the industry – effective process optimization and cost reduction. How can medical treatment become more affordable without affecting the quality of patient treatment? Seems like 3D-technology can help with that.
3D-printers in healthcare
3D printing technology looks very promising for the medical and healthcare industry. When it comes to 3D printers, many of us probably envision a futuristic hospital with new organs, joints, connective tissue and skin printed on an industrial scale. Modern medicine is still a long way off from this image, but that doesn't mean a 3D printer can’t be a valid medical tool. At the moment, 3D printing is successfully used in many fields of medicine.Prosthetics and orthotics production
3D printers have firmly established themselves in prosthetics and orthotics. According to World Health Organization (WHO) about 35–40 million people require prosthetics and orthotics services and the number is increasing due to a range of factors. Moreover, about 2.5 billion people need one or more assistive products, such as mobility or hearing device, and with the aging population this number is estimated to reach 3.5 billion by 2050.
Conventional assistive products, precisely prosthetics, are expensive, take quite long time to produce and need regular manual adjustments.
3D-printers help make prosthetics cost-effective, reduce manufacturing time while being completely bespoke.Implants
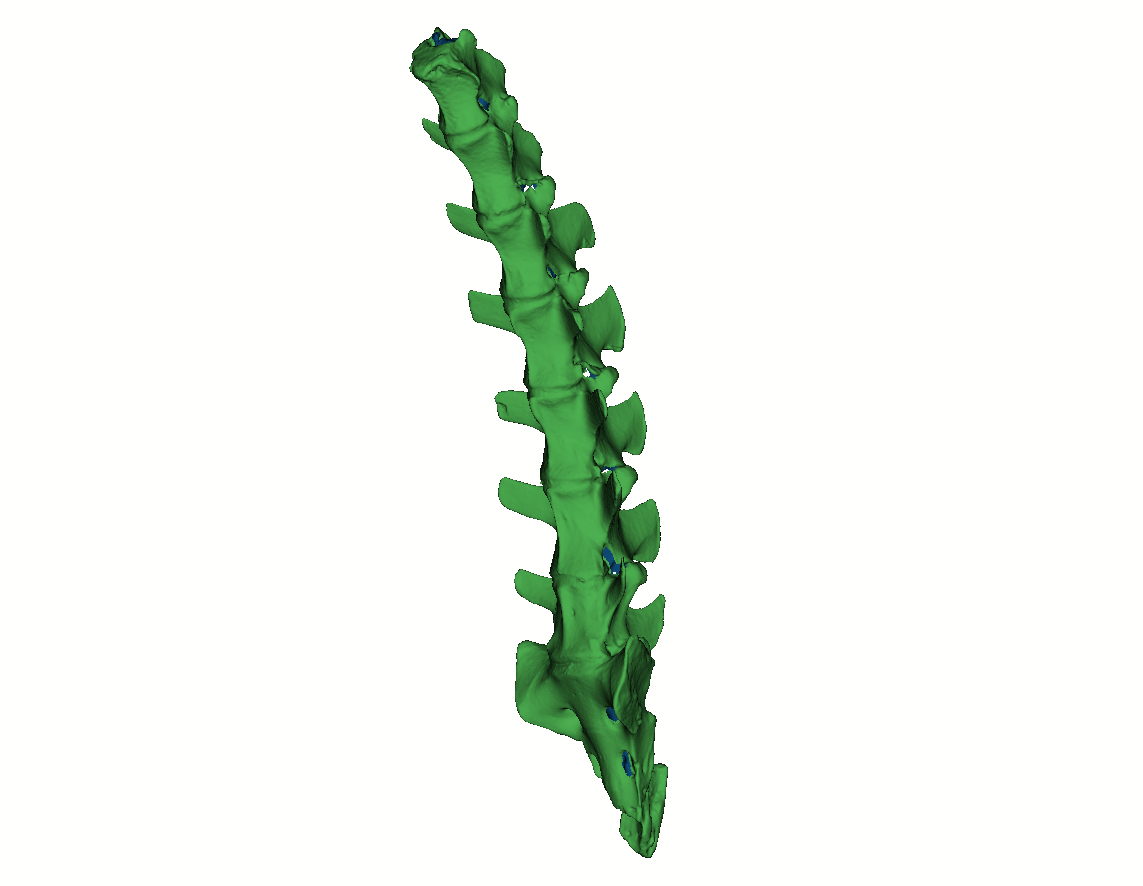
As with prosthetics and orthotics, implants (dental, spinal, hip) are expensive and labor intensive to produce. Printing makes it possible to achieve personalized production for less money.Anatomical models for doctors and medical students
Modern 3D-printers can replicate body parts and organs with high accuracy and realism. Anatomical models allow medical students as well as doctors to practice their skills. Simulation of surgeries minimizes risks and helps to prepare for complicated surgeries beforehand. For example, 3D-printing technology along with MRI and ultrasound imaging can assist specialists in preparing for fetal and babies’ surgical treatment.
Portable 3D-scanners in healthcare
When looking at the numerous publications on the Internet, it may seem that 3D scanning technology is not as prevalent in medicine as 3D printing. That's a bit of an erroneous judgment that comes from the fact that 3D-scanners were introduced later to the medical community than other 3D-technologies. Nevertheless, they are confidently showing their effectiveness and get adopted by more hospitals and clinics.Implants, Orthotics and Prosthetics
We mentioned previously that 3D-printers produce tailor-made prosthetics and implants and significantly expedite production time. 3D scanners significantly improve this production chain. Measurements of the human body are made quickly, accurately and what’s more important they are contactless. Done once, a digital copy of a limb can be used numerous times – the doctors can amend it right in the CAD software according to the patient’s changes, tracking the progress. This is especially convenient when doing medical treatment for children.
Additionally, 3D-scans can optimize bureaucratic regulations in some countries which require prosthetic specialists keep extensive medical records regarding patient treatment, including… the storing casts for years.
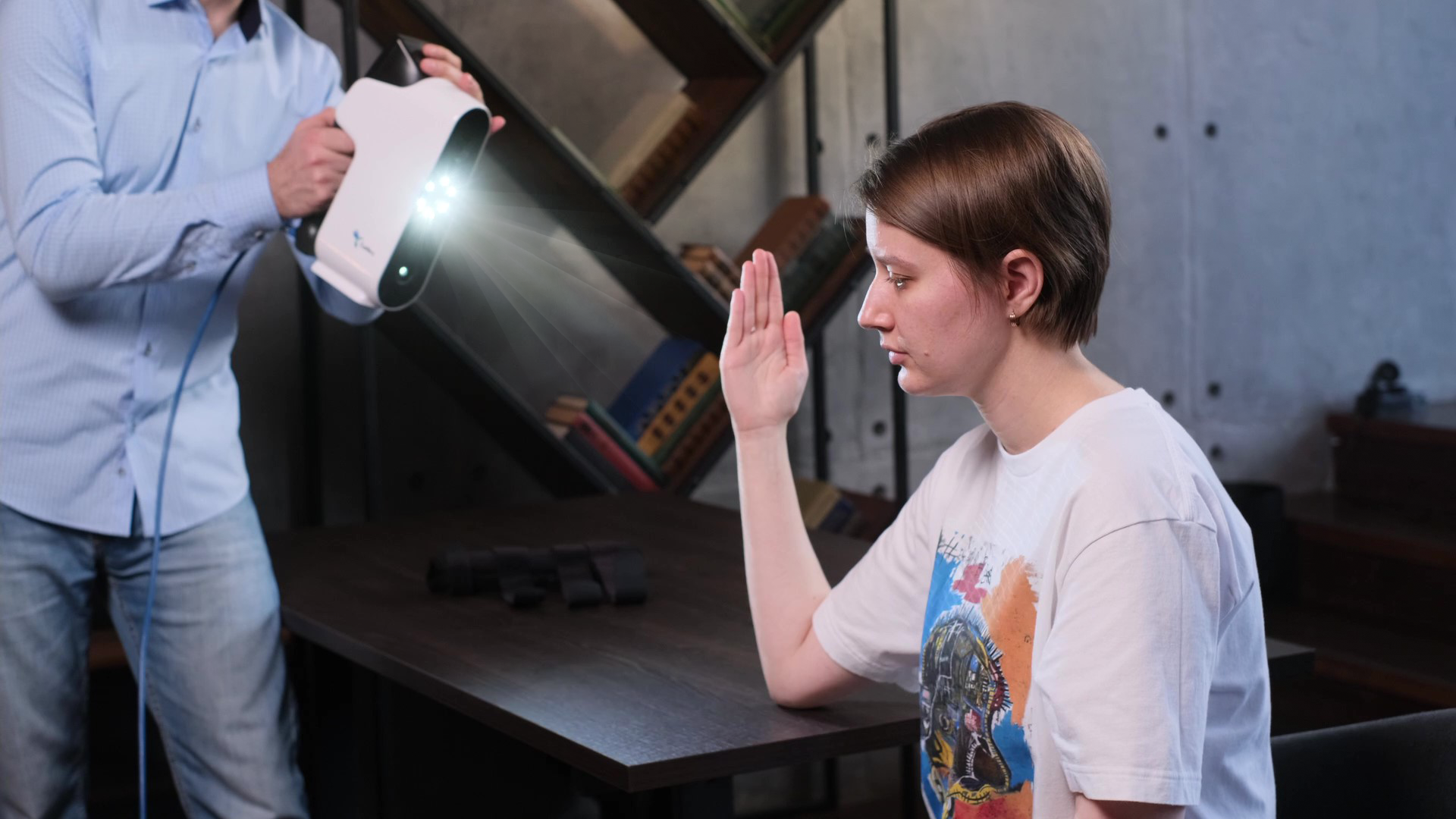

Dentistry
In dentistry, 3D-scanners have gained much popularity. They can be used for treatment and diagnosis. 3D-scanners help make ceramic crowns, tooth prosthesis and teeth models.
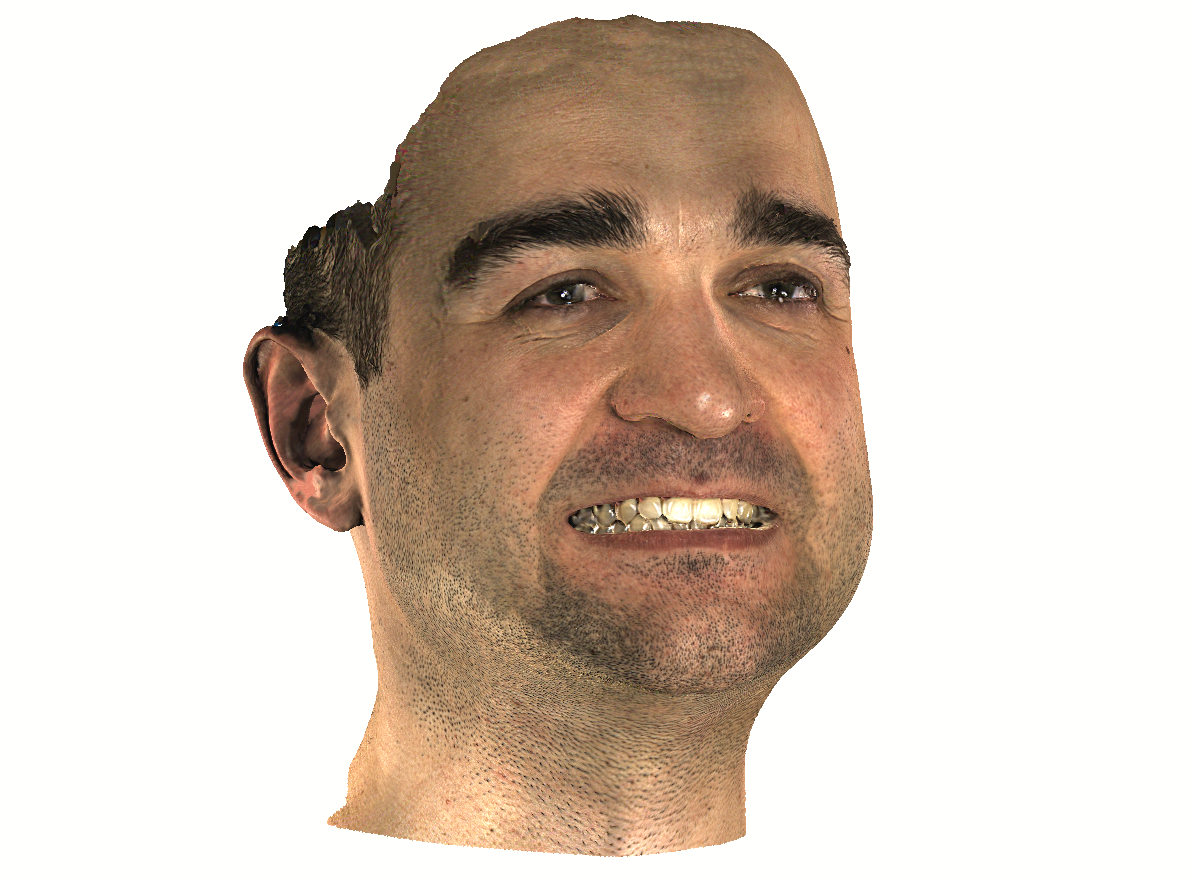

Diagnosis
The accuracy with which 3D scanners digitize the human body allows them to be used in patient diagnosis. Modern 3D scanners collect not only geometry, but also texture data, which makes them applicable for diagnosing skin diseases, musculoskeletal disorders (e.g. scoliosis), certain types of cancer.
Patient monitoring
3D-scanners are excellent for monitoring a patient's healing process. Rapid non-invasive digitization, which does not require specially equipped rooms, helps doctors simplify the process of documenting the patients’ recovery. One of the primary applications is to monitor burnt victims in cases when physical contact in not permitted.
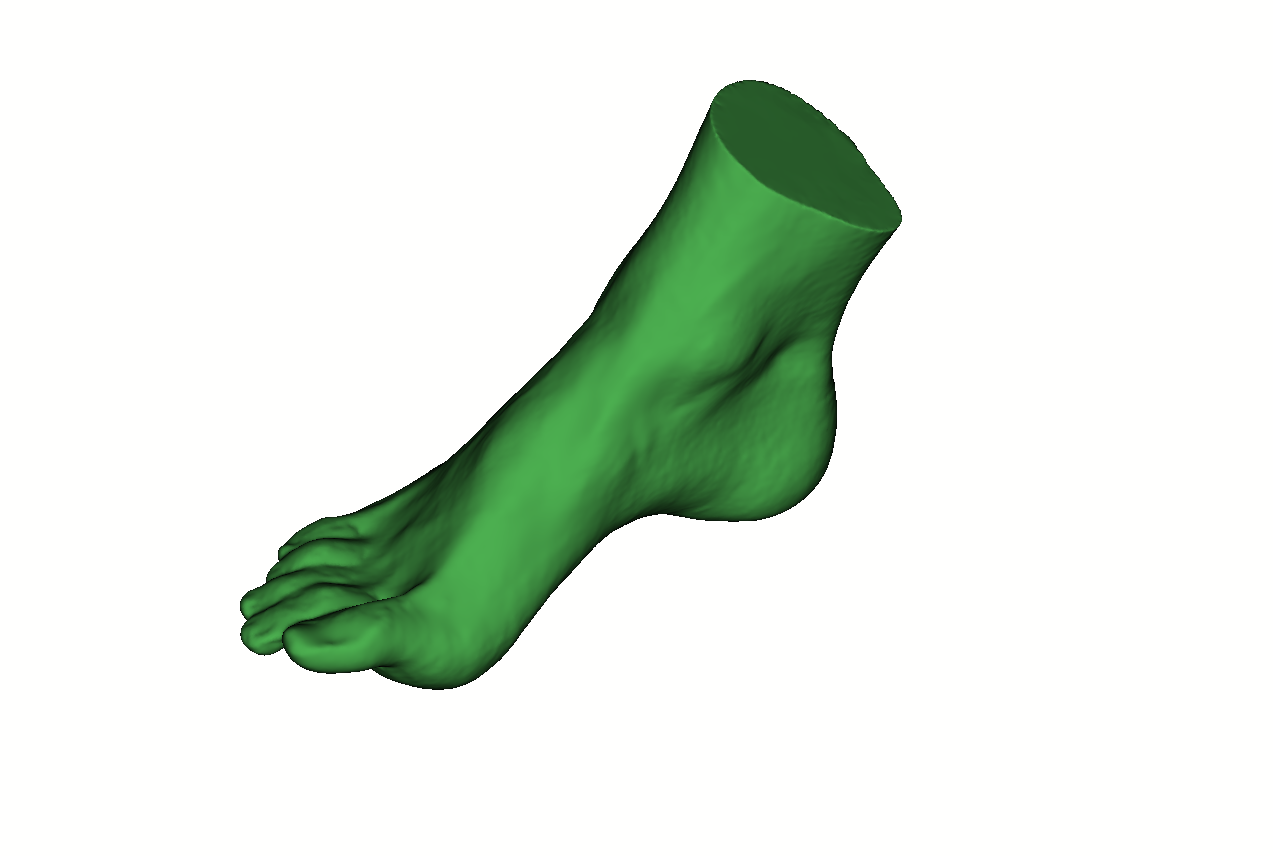

Medical use-cases with Calibry 3D-scanners
Our portable 3D-scanners are notable for successful use cases in pediatric orthopedics, plastic surgery and prosthetics.
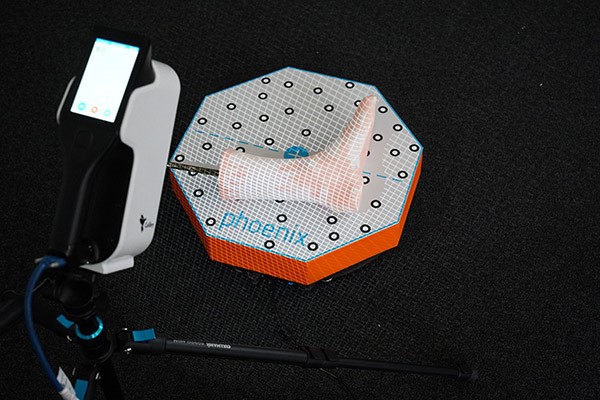
A German clinic with the help of our partner developed a full process chain incorporating 3D-technologies aimed at optimizing a physician’s workload. With the help of Calibry 3D scanner, Calibry Nest and Geomagic Wrap software, 3D printer Tractus orthopedists’ workload in production of orthosis was decreased by 40%. You can read a case study of Calibry 3D scanner in orthopedics on our website.

A French non-profit organization used handheld 3D-scanner Calibry to reduce the cost of prostheses for children with agenesia. Robotized prosthesis are expensive and they don’t always adapt to the morphology of the child’s limb. Aesthetic prosthesis are able to hide the disability but cannot help in the everyday routine. The prostheses produced with Calibry 3D-scanner and a 3D-printer provided all the necessary functionality at the cost of 50 euros per item. More information is available in our article on affordable and customized prostheses with Calibry 3D-scanner.
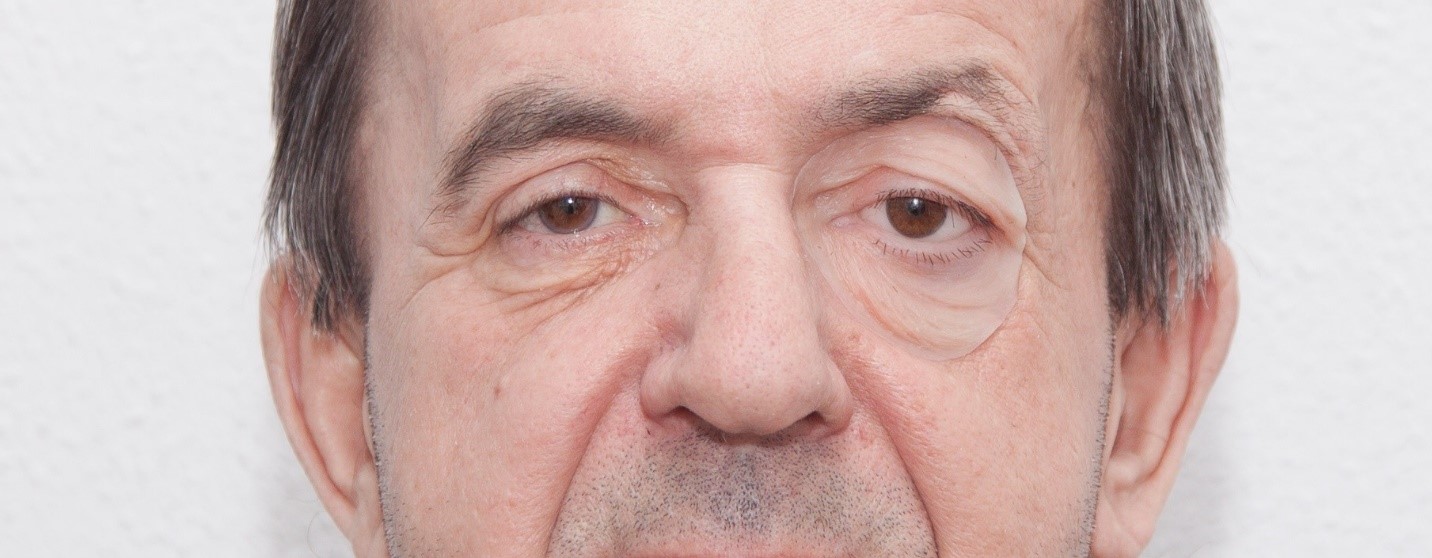
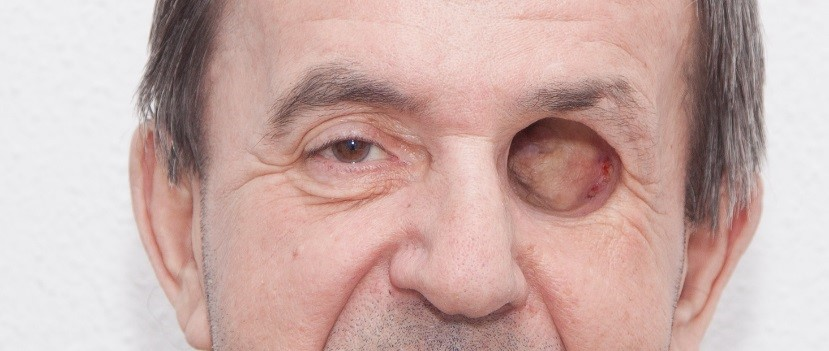
Due to the accurate digitization of body parts, 3D scanners are often used for facial prosthetics where not only functional but also aesthetic characteristics are important.
Artificial eyes, ears and facial parts are created on the basis of an exact copy of the face. Printed on a 3D printer, they are practically indistinguishable from the real ones, while the price of production is much lower than traditional methods.

Benefits of 3D technologies in healthcare
3D-technologies have a number of undeniable advantages that have led more and more physicians to adopt it:
-
Quicker turnaround time (while conventional production methods take days or even weeks, 3D-technologies need a couple of hours)
-
Reduction of contact (convenient for children, patients with burnt skin and etc)
-
Measurements, patient monitoring and diagnosis can be done almost on-the-go, because no specially equipped laboratories are required.
-
-
3D scans aka digital copy of a patient can be easily sent to other doctors (for a medical consultative committee for example)
Analyzing Return on Investment (ROI) of 3D-scanners in medicine
The benefit of 3D scanning for medicine can be measured not only by the concepts of “doctor convenience” and “patients’ comfort”, but also in solid numbers. Since 3D scanners are most actively used in assistive technologies (orthopedics, prosthetics), let's evaluate the ROI of this area of medicine:
| Indicators | Fully conventional method | Partly conventional | Fully digital |
| method description | measurement, hand modelling the cast, casting the form and making adjustments, vacuum thermoforming of the orthosis shell | measurement, cad design, 3d-printing | 3d-scanning, cad design, 3d-printing |
| number of specialists | 2-3+ | 2-3 | 1-2 |
| time | few days or even weeks | 24-12 hours | 8-4 hours |
| cost | cost of all materials + wages of professionals | cost of all materials + wages of professionals + cost of 3d-printing | cost of all materials + wages of professionals + cost of 3d-printing |
| price of the prosthesis/orthosis | 1000-8000 USD | up to 50% cheaper | up to 70% cheaper |